CAREER PATHS
Medical Assistant vs. Nurse: Key Differences Explained
-
 EveryNurse Staff
EveryNurse Staff
- Last Updated: 05/09/2023

The healthcare industry is a complex and highly regulated field. It is common for individuals to be unaware of the various roles and responsibilities that exist within this sector. Medical assistants and nurses are two positions that are critical to the provision of quality care. These professions have different educational and training requirements as well as distinct job responsibilities. Let’s explore the differences between a medical assistant and a nurse, what their roles are, and where they work.
Medical Assistant Vs. Nurse
Healthcare is a complex and dynamic field that requires a team of professionals to provide quality care to patients. Two essential members of this team are medical assistants and nurses. While both medical assistants and nurses play a crucial role in providing patient care, their roles and responsibilities differ.
The Role of a Medical Assistant
A medical assistant is an essential member of a healthcare team whose primary responsibility is to assist with clinical and administrative duties. Medical assistants work in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and physician offices. They are often the first point of contact for patients and play a vital role in ensuring that patients receive quality care.
Medical assistants perform a wide range of duties, from taking vital signs and administering medications to preparing patients for medical procedures. They also perform various clerical tasks, such as scheduling appointments, maintaining medical records, and coordinating patient care.
The Role of a Nurse
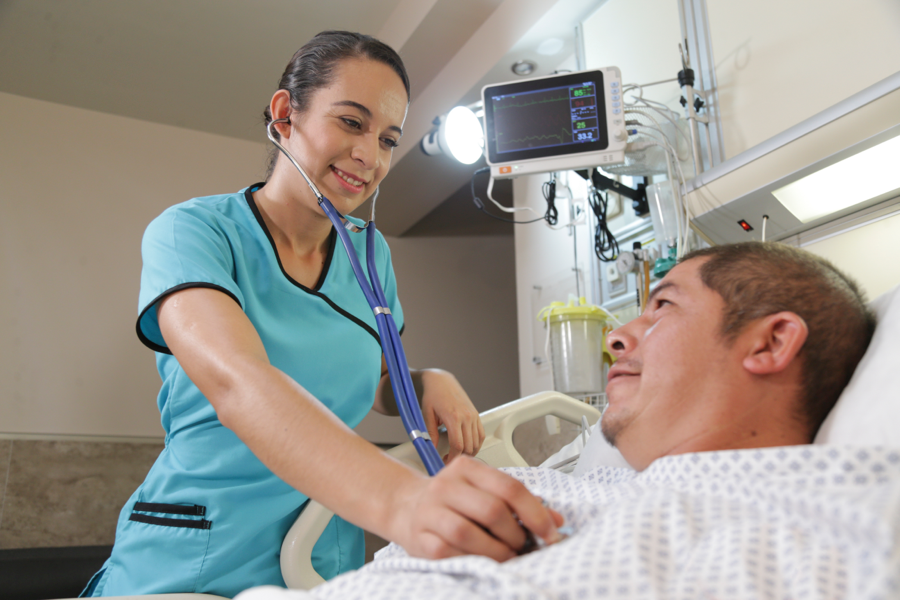
A nurse, on the other hand, is an individual who has completed a formal education program in nursing and is licensed to practice nursing. Nurses work in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities. They are responsible for providing patient care, assessing and diagnosing medical conditions, and developing and implementing care plans.
Nurses take a holistic approach to patient care, considering the physical, emotional, and social aspects of a patient’s well-being. They work closely with patients and their families to provide education and support throughout the healthcare process.
In addition to their clinical duties, nurses also play an essential role in healthcare administration and research. They are often involved in developing and implementing healthcare policies, conducting research studies, and educating the public about healthcare issues.
Educational Requirements for Medical Assistants and Nurses
To become a medical assistant or nurse, individuals must meet specific education and licensure requirements.
Medical Assistant Education
Medical assistants play a vital role in the healthcare industry, performing both clinical and administrative duties. The education requirements for a medical assistant vary by state and employer; however, most medical assistants complete a formal medical assisting program or receive on-the-job training.
Medical assisting programs typically take one to two years to complete and may be offered at community colleges, vocational schools, or technical institutes. These programs cover topics such as medical terminology, anatomy and physiology, pharmacology, and medical office procedures. Students also gain hands-on experience through clinical rotations, where they work in healthcare settings under the supervision of experienced medical professionals.
Medical Assistant Education and Certification
Some employers may require their medical assistants to obtain certification. Certification is available through various organizations, such as the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) and the National Healthcareer Association (NHA). Certification demonstrates a medical assistant’s competency and knowledge of clinical and administrative procedures. To become certified, medical assistants must pass an exam that covers topics such as anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, and medical law and ethics.
Nursing Education and Licensure
There are various education paths to becoming a registered nurse, including completing a nursing diploma program, an associate degree in nursing (ADN), or a bachelor’s degree in nursing (BSN).
Nursing diploma programs are typically offered by hospitals and take about three years to complete. ADN programs are offered at community colleges and take about two years to complete, while BSN programs are offered at universities and take four years to complete. All nursing programs require students to complete clinical rotations to gain hands-on experience in healthcare settings.
Upon completion of a nursing program, individuals must pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN) to become a licensed registered nurse (RN). The NCLEX-RN is a standardized exam that tests a nurse’s knowledge and competency in areas such as patient care, pharmacology, and medical procedures. Nurses may also choose to further their education by obtaining a master’s degree or doctoral degree in nursing.
Scope of Practice for Medical Assistants and Nurses
Medical assistants and nurses play crucial roles in the healthcare industry. They are responsible for providing patient care and ensuring that patients receive quality medical attention. While both professions are important, their scope of practice varies based on their education, training, and state laws.
Medical Assistant Scope of Practice
The scope of practice for medical assistants varies by state and employer. In general, medical assistants are not authorized to assess or diagnose medical conditions, prescribe medication, or perform invasive procedures.
However, medical assistants are responsible for a range of tasks that help physicians and nurses provide quality care to patients. They may take patient histories, measure vital signs, assist with examinations, and perform basic laboratory tests. They may also administer medications, injections, and immunizations under the direction of a physician or nurse.
Medical assistants must work within the boundaries of their training and education. They are not licensed healthcare professionals, but they play a critical role in supporting the healthcare team and ensuring that patients receive the care they need.
Nursing Scope of Practice
The scope of practice for nurses is determined by state laws and regulations. Registered nurses (RNs) are authorized to assess and diagnose medical conditions, develop and implement care plans, and administer medications and treatments.
RNs work closely with physicians to ensure that patients receive quality care. They may also supervise other healthcare professionals, such as licensed practical nurses (LPNs) and medical assistants. RNs may specialize in an area of practice, such as pediatrics, emergency medicine, or critical care.
LPNs, on the other hand, have a more limited scope of practice. They are authorized to perform basic nursing tasks, such as measuring vital signs, administering medications, and providing basic patient care. However, they are not authorized to assess or diagnose medical conditions, develop care plans, or perform complex medical procedures.
Work Settings and Job Responsibilities
Where Medical Assistants Work
Medical assistants work in various healthcare settings, such as physician offices, clinics, hospitals, and long-term care facilities. They may also work in specialty practices such as podiatry or dermatology offices. In physician offices, medical assistants may be responsible for greeting patients, taking vital signs, and preparing patients for examination.
In clinics, medical assistants may assist with minor medical procedures such as removing sutures or changing dressings. In hospitals, medical assistants may work in various departments such as emergency, pediatrics, or surgery, and may be responsible for preparing patients for procedures, administering medications, and assisting with patient care.
Where Nurses Work
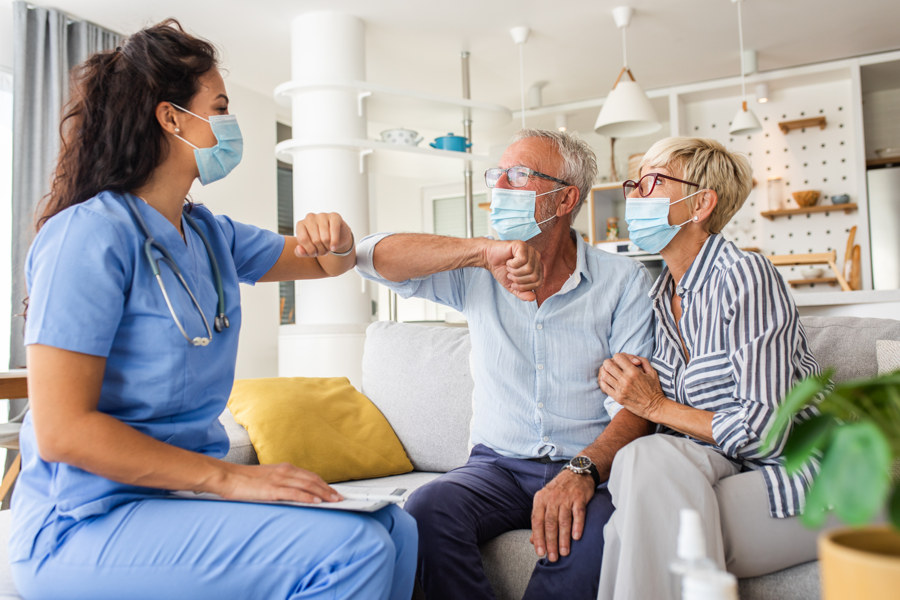
Nurses work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, and schools. They may also work in specialty practices such as oncology or cardiology. In hospitals, nurses may work in different units such as intensive care, labor and delivery, or medical-surgical.
In clinics, nurses may provide primary care services such as health screenings and immunizations. In long-term care facilities, nurses may be responsible for managing the care of residents and administering medications. School nurses may provide care to students with chronic medical conditions and administer medications or treatments as needed.
Comparing Job Duties of Medical Assistants and Nurses
There is some overlap in the job duties of medical assistants and nurses. Both professions work to provide quality care to patients, but the finer details of their job duties may differ. Medical assistants are responsible for maintaining medical records, preparing patients for examination, administering medications, and providing patient education.
They may also assist with minor medical procedures and perform basic laboratory tests. Nurses, on the other hand, may assess and diagnose medical conditions, develop care plans, administer medications and treatments, and provide patient education. They may also supervise other healthcare professionals and provide leadership in healthcare settings.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Advancement Opportunities for Medical Assistants
Advancement Opportunities for Nurses
Registered nurses can further their education and obtain a master’s or doctoral degree in nursing, which may lead to career advancement opportunities. Nurses may also choose to specialize in a particular area of practice, such as oncology, pediatrics, or critical care. Additionally, experienced nurses may be promoted to management or leadership positions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medical assistants and nurses are critical members of a healthcare team. While these professions share some commonalities, they have distinct roles and responsibilities. Medical assistants are responsible for providing clinical and administrative support to physicians and nurses, while nurses are responsible for providing patient care, assessing and diagnosing medical conditions, and developing and implementing care plans. Both professions offer career advancement opportunities through further education and specialization.